Traveling Luck for Gambia. Gambia, Africa
The Gambia is located in Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal.
Land in The Gambia is flood plain of the Gambia River flanked by some low hills.
Gambian land covers an area of 11300 square kilometers which is slightly less than twice the size of Delaware
Gambia has borders with Senegal for 740km.
 Gambian national flag (Flag of Gambia)
Gambian national flag (Flag of Gambia)
As for the Gambian climate; tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May).
Gambian(s) speak English (official), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars.
Places of note in Gambia
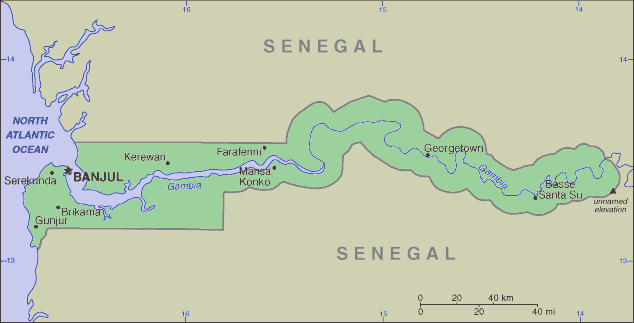 Gambian map
Gambian map
Regions of Gambia
The Gambia gained its independence from the UK in 1965; it formed a short-lived federation of Senegambia with Senegal between 1982 and 1989. In 1991 the two nations signed a friendship and cooperation treaty. A military coup in 1994 overthrew the president and banned political activity, but a 1996 constitution and presidential elections, followed by parliamentary balloting in 1997, completed a nominal return to civilian rule. The country undertook another round of presidential and legislative elections in late 2001 and early 2002. Yahya A. J. J. JAMMEH, the leader of the coup, has been elected president in all subsequent elections.
The Gambia has no significant mineral or natural resource deposits and has a limited agricultural base. About 75% of the population depends on crops and livestock for its livelihood. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the processing of peanuts, fish, and hides. Reexport trade normally constitutes a major segment of economic activity, but a 1999 government-imposed preshipment inspection plan, and instability of the Gambian dalasi (currency) have drawn some of the reexport trade away from The Gambia. The government's 1998 seizure of the private peanut firm Alimenta eliminated the largest purchaser of Gambian groundnuts. Despite an announced program to begin privatizing key parastatals, no plans have been made public that would indicate that the government intends to follow through on its promises. Unemployment and underemployment rates remain extremely high; short-run economic progress depends on sustained bilateral and multilateral aid, on responsible government economic management, on continued technical assistance from the IMF and bilateral donors, and on expected growth in the construction sector.
Gambian natural resources include fish, titanium (rutile and ilmenite), tin, zircon, silica sand, clay, petroleum
almost an enclave of Senegal; smallest country on the continent of Africa
Gambian religion is Muslim 90%, Christian 9%, indigenous beliefs 1%.
Natural hazards in The Gambia include drought (rainfall has dropped by 30% in the last 30 years).
Travel Advice for Gambia
Gambia, TheSUMMARY
- You should not travel by road from The Gambia to Casamance in southern Senegal because of an increase in fighting between rebel factions involving the Senegalese armed forces.
- Care should be taken when driving or walking on roads, particularly at night, due to unpredictable driving standards and lack of street lighting.
- Malaria is prevalent in The Gambia. You should seek medical advice about taking anti-malarial medication before, during and after your visit. In addition, you should take precautions to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes. Please see the Health Section of this travel advice for more details.
- The threat from terrorism is low, but you should be aware of the global risk of indiscriminate terrorist attacks, which could be against civilian targets, including places frequented by foreigners.
- Around 50,000 British nationals visit The Gambia each year. Most visits are trouble-free. The main types of incident for which British nationals require consular assistance in The Gambia are for replacing lost and stolen passports and financial assistance. Crime against tourists is increasing and you should take sensible precautions and remain vigilant in public places.
- We strongly recommend that you obtain comprehensive medical and travel insurance before travelling. You should check any exclusions, and that your policy covers you for the activities you want to undertake. Please see: Travel Insurance.
SAFETY AND SECURITY
The Gambia Country Profile.
National Assembly elections took place on 25 January 2007 and passed off peacefully.
You are advised to avoid political gatherings and demonstrations.
You should not stay or travel in the Casamance region west of Kolda. This includes travel by road into the region from The Gambia. For further details please see the travel advice for Senegal.
You can drive on a UK driving licence for up to three months.
The EU has published a list of air carriers that are subject to an operating ban or restrictions within the community. You should check the following link to see whether this will affect your travel: http://europa.eu.int/comm/transport/air/safety/flywell_en.htm
LOCAL LAWS AND CUSTOMS
The Gambian authorities will take strong action against anyone importing, exporting or found in possession of drugs or contraband. You should not accept packages on behalf of anyone without knowing the contents.
ENTRY REQUIREMENTS
HEALTH
GENERAL
Money
You are advised to bring traveller’s cheques or cash to The Gambia because only a few places accept credit cards. Bureaux de Change and local banks do not.

 Search
Search Gambia country profile
Gambia country profile Travel advice for Gambia
Travel advice for Gambia